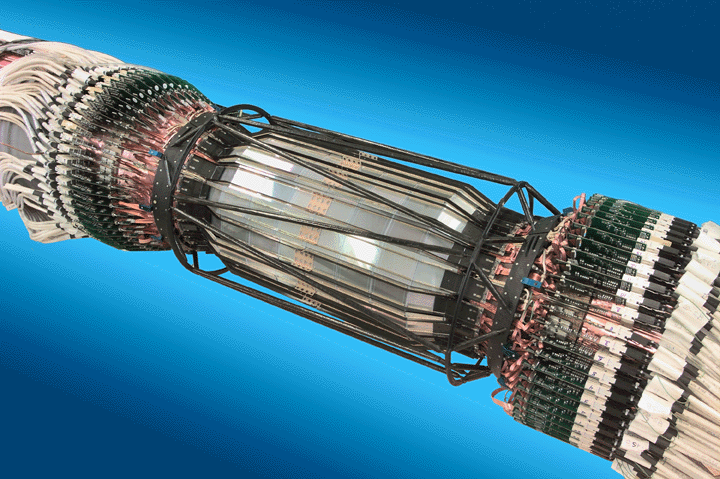
The Silicon Vertex Tracker for the BaBar experiment at SLAC.
This 5 layer silicon detector provides excellent resolution and is
critical for measuring CP violation.
This page has a variety of things associated
with the new brochure.
| text received | image received | |
| abbott | x | x |
| abraham | x | x |
| baron | x | x |
| branch | x | x |
| cowan | x | x |
| doezema | x | x |
| furneaux | x | |
| gutierrez | x | x |
| henry | x | x |
| johnson | x | |
| kao | x | x |
| kantowski | x | x |
| leighly | x | x |
| macgorman | x | x |
| mason | x | x |
| milton | x | x |
| morrison | x | x |
| mullen | x | x |
| murphy | x | x |
| parker | x | x |
| romanishin | x | x |
| ryan | x | |
| rust | none | |
| santos | x | x |
| shafer-ray | x | x |
| skubic | x | x |
| strauss | x | x |
| wang | x | x |
| watson | x |
PDF version
of text.
Other Images:
Here is a page of other
possibly useful images

The Silicon Vertex Tracker for the BaBar experiment at SLAC.
This 5 layer silicon detector provides excellent resolution and
is
critical for measuring CP violation.
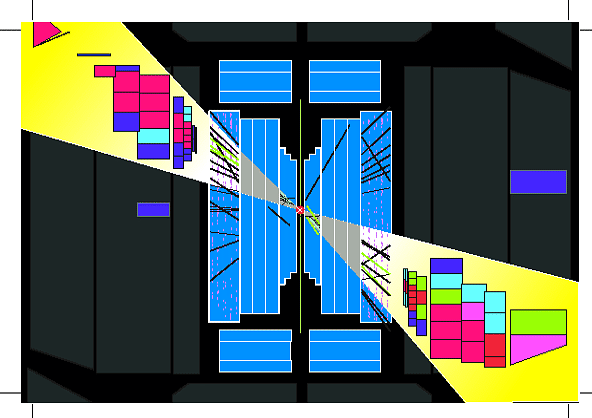
Event display showing the highest transverse energy jet found in D0.
These high energy jets probe very small distance scales and allow
us to search for quark sub-structure.
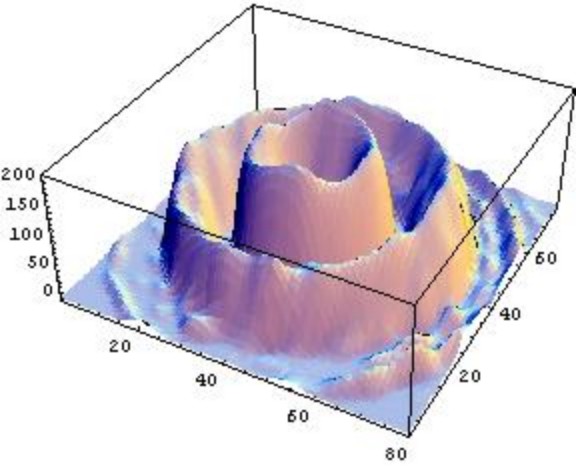
A 2-dimensional image of the intensity profile of a laser beam in a
high-order Laguerre-Gaussian mode. Using diffractive optics,
we make
these beams with previously unobtainable mode purity. One characteristic
of these beams is their ring and multiple-ring nature. Using
the dipole
force, atoms can be trapped in the intensity valleys shown in the figure.
These concnetric rings of ultracold atoms can be used for studies of
vortices in Bose-Einstein condensation.
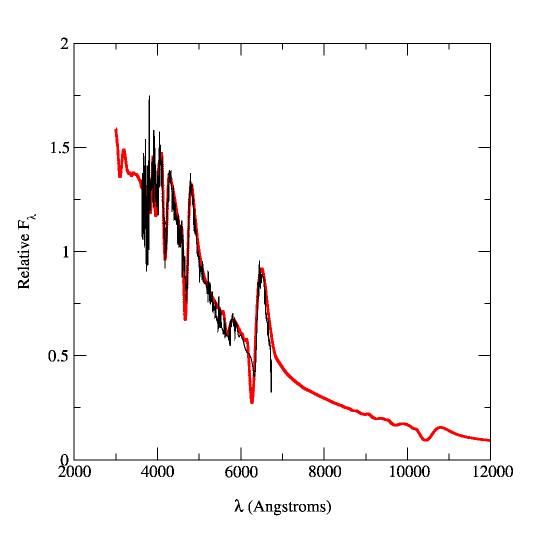
A model fit (red line) to the observed spectrum of SN 1993W. SN 1993W
was
a normal Type IIP supernovae and from fits like the one displayed above
we
can determine the supernova's distance (for cosmology), its composition
(for the theory of stellar and galactic chemical evolution), as well
as
the properties of the explosion. The model calculated above included
very
detailed physical properties and took about 20 hours on a
parallel supercomputer to
calculate.
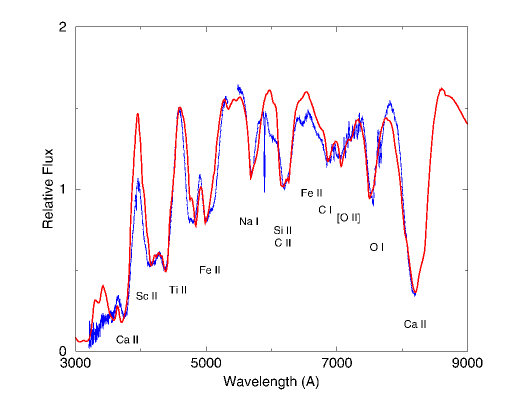
An observed spectrum (blue line) of the Type Ic supernova 1994I
obtained by A. V. Filippenko at the Lick Observatory is compared to
a
theoretical spectrum (red line) calculated with our SYNOW supernova
synthetic-spectrum code. Ions that are responsible for the most
conspicuous supernova absorption features are indicated. The
narrow
absorption near 5900 Angstroms is produced not by the supernova but
by
interstellar sodium.
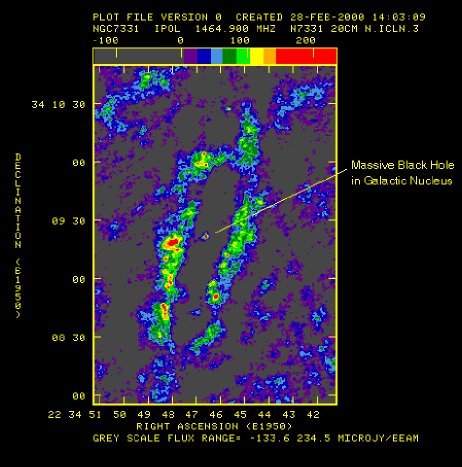
Galaxy NGC 7331, located approximately 30 million light years away,
appears to contain a Massive Black Hole. This black hole was
detected
by researchers here at OU (see ``Discovery of a Nuclear X-ray Source
in
NGC 7331:'' ApJ Letters 508, L33 (1998).)
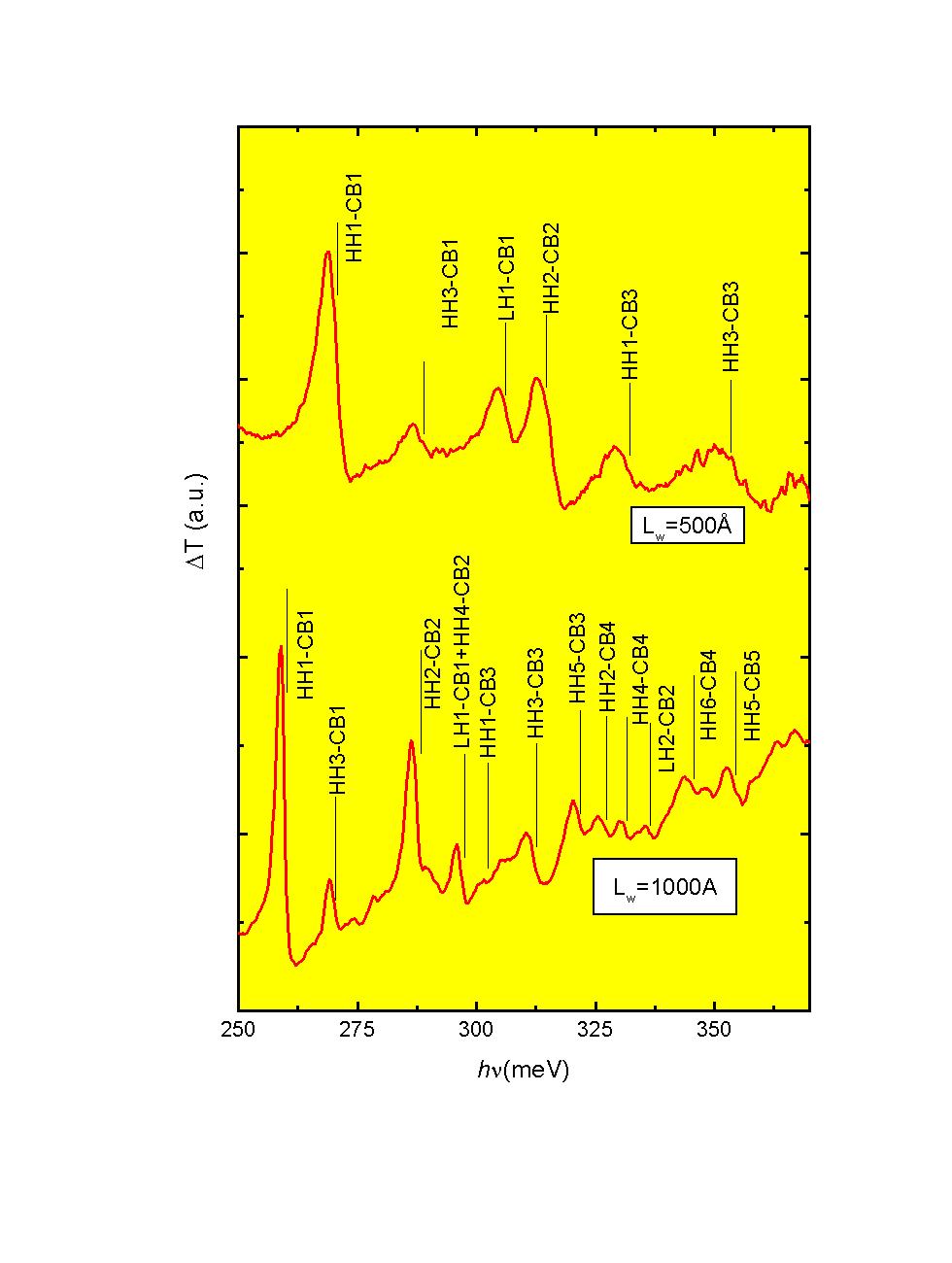
A plot of the spectra for excitons (electron-hole pairs) in parabolic
InSb quantum wells with different widths. The samples were
grown at OU. The figure is labeled by the transitition type, between
heavy hole (HH) or light hole (LH) states to conduction band (CB) electron
states.
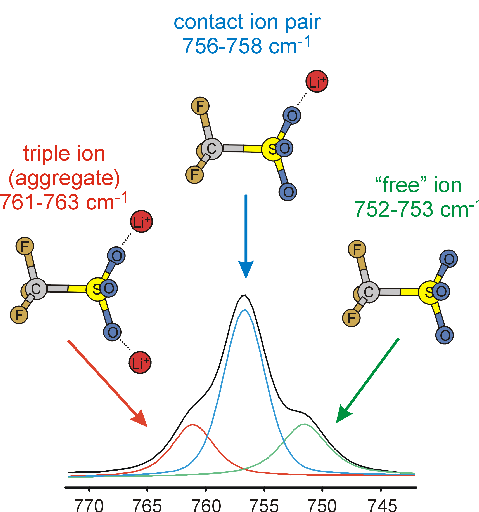
A plot of the IR spectrum of a lithium-ion conducting polymer sample.
The ionic association of the trifolate anion affects peak position and
intensity.
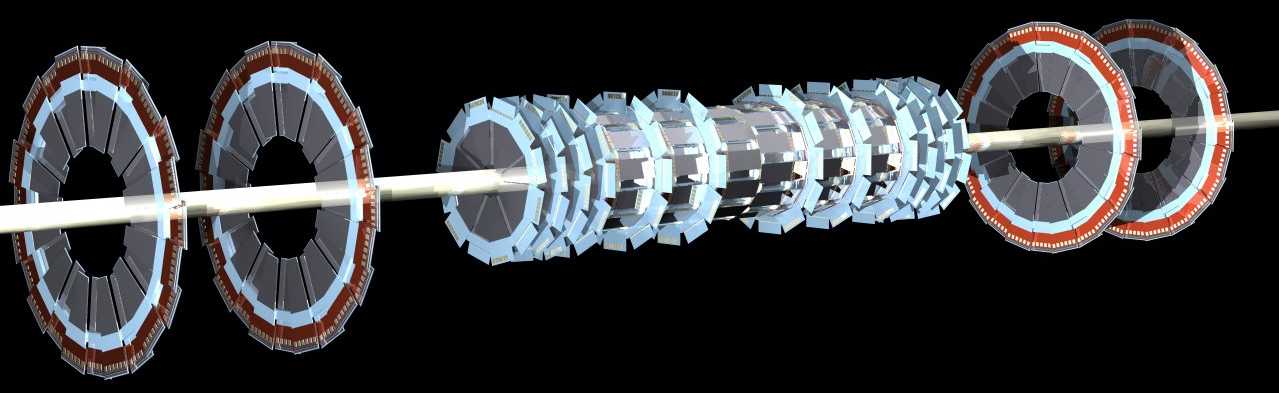
This diagram shows the new silicon microstrip vertex
detector. Its purpose is to find and identify particles
with lifetimes of about 1 ps. The majority of particles
with this lifetime, are particles that are composed of
b-quarks. Identifying these particles will be useful
in the search for the Higgs boson since its dominant
decay mode is to these particles.
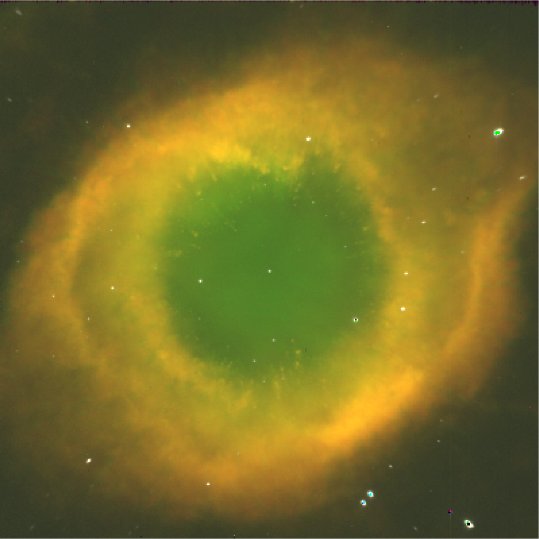
When stars in the 1-8 solar mass range reach the end of their
evolution, they shed outer portions of their atmospheres. The dying
star left behind shrinks and gets hotter, and UV light from it cause
the outer ring of gas to glow, making it easy to study the chemical
makeup of the gas. Planetary nebulae typically show evidence of large
carbon and nitrogen abundances, consistent with the idea that the
material being shed contains the nuclear products manufactured during
the star's life. Therefore, we are witnessing an event in which stellar
nuclear products along with stellar gas are cycled back into the
interstellar medium, causing the latter to become chemically richer.
This image of NGC 7293, the Helix Nebula, was taken by Reginald Dufour
of Rice University, using a CCD camera.
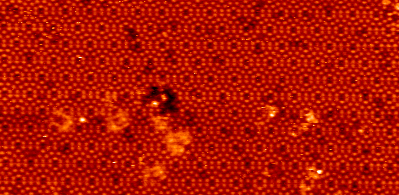
An STM image of the silicon (111) 7x7 reconstruction.
The image size is 40 nm by 20 nm and the color scale is 0.3 nm.
The lighter dots that form the pattern are individual atoms of silicon.
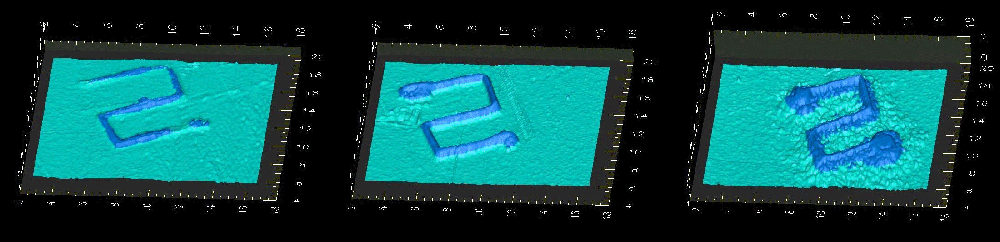
AFM (Atomic Force Microscope) images of NSOM
(Nearfield scanning optical microscopy) lithographt generated
patterns. The pattern on the
left was produced with no optical illumination. The middle and right
patterns were produced with optical illumination with the right pattern
having an increased dither amplitude compared to the middle pattern.
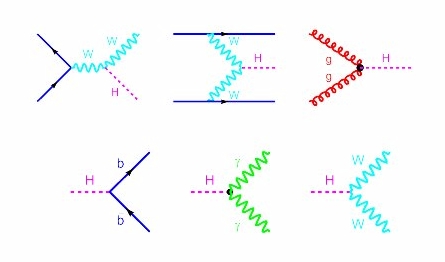
Production and decay modes for the Higgs particle.
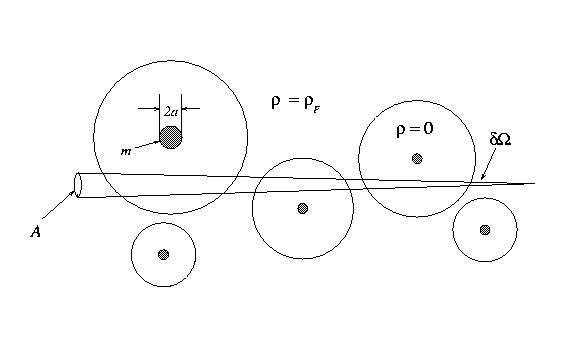
A sketch of a radiation beam of cross-section "A" propagating through
a "swiss-cheese" universe from a distant source to an observer. Understanding
how local inhomogeneities affect the propagation of light is important
in determining cosmological parameters from data.
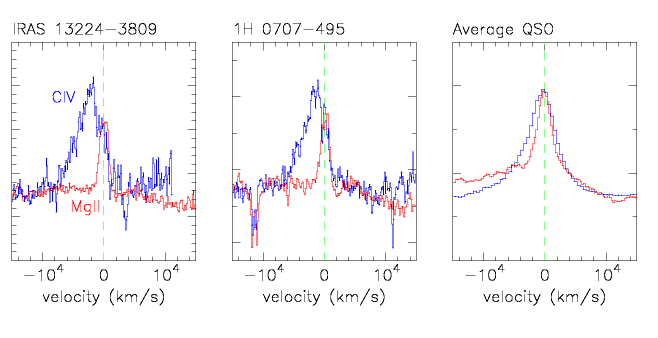
The rescaled representative high-ionization line CIV
superimposed on the representative low-ionization line MgII
as
a function of velocity, for two extreme narrow-line
Seyfert 1 galaxies (NLS1s) and the average quasar.
The average quasar high-ionization line is slightly broader and
slightly blueshifted compared with the low-ionization line. In
contrast, the low-ionization lines in NLS1s are much narrower and the
high-ionization lines are strongly blueshifted.
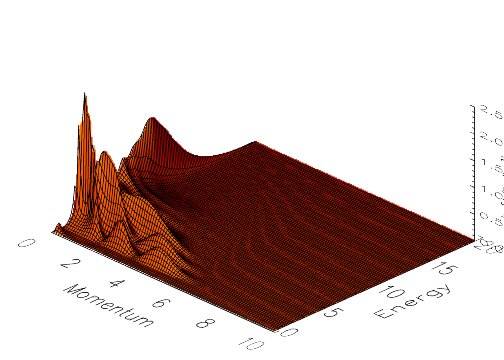
Calculated dielectric function of an impure two-dimensional
electron gas, $ \epsilon ( k, \omega )$, in a magnetic
field. Scattering is due to remote ionized impurities
and the filling factor is $\nu = 6$. This calculation
includes the full wavenumber and frequency dependence
of the electron response functions.
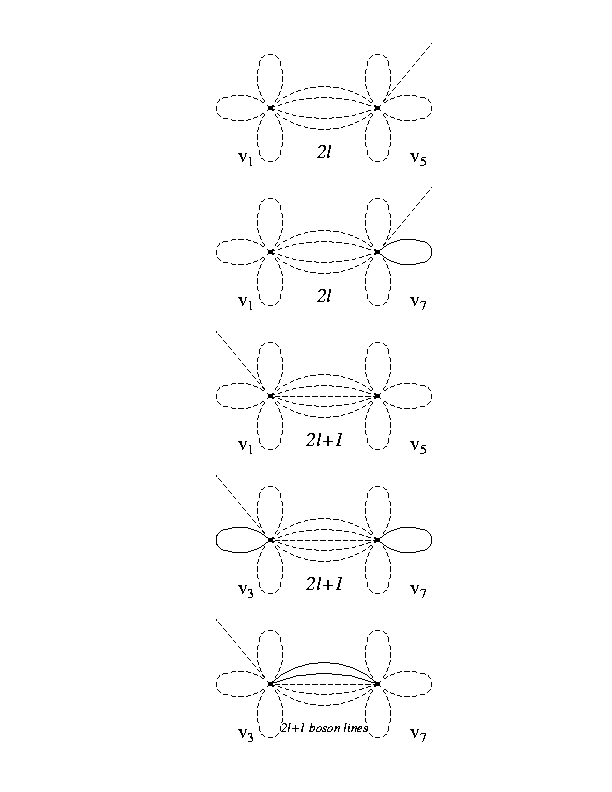
Five of the Feynman graphs that contribute to the calculation
of a two dimensional supersymmetric quantum field theory. Some forms
of such a theory can break parity symmetry (which we know is broken in
nature) but preserve supersymmetry. Such calculations are notoriously
difficult to perform with convential perturbation theory, but can be approached
by expanding in powers of the degree of the nonlinearity of the interaction.
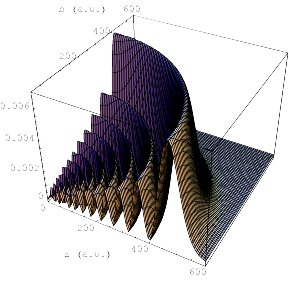
The radial transition density for the 17d and 18p Rydberg states of
calcium. When a rare-gas projectile approaches a Ca atom in the 17d
state,
its encounter with regions of high transition density provide alternate
quantum-mechanical ``paths'' by which it can induce the Rydberg electron
to
undergo a transition to the 18p state. Such collisions represent a
new
realization of the quintessentially quantum mechanical ``double-slit
interference'' pheomena, as discussed in "Rydberg Electron
Interferometry," Physical Review Letters, 84, 1415 (2000).
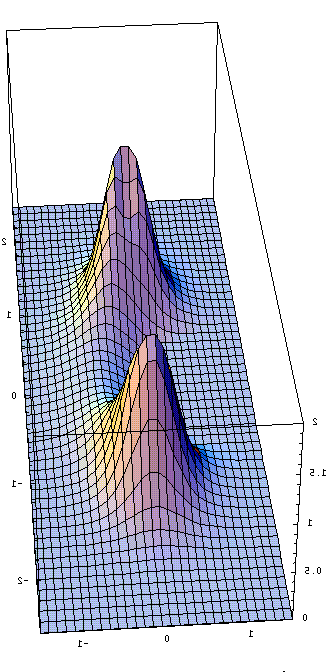
A skyrmion is a charged ump or bubble in the electron spin field in
a two dimensional electron gas. Plotted here is the energy density
as a function of position for two interacting skyrmions. Calculating
their energy of interaction is difficult since the system is nonlinear.
The longitudinal resistance is displayed versus magnetic field for a variety of different temperatures. It is interesting to note that even at temperatures as high as 25K the integer quantum Hall effect can still be seen in this InSb sample.
The quantum phase transition between the quantum Hall state and a high
field insulating state is demonstrated by these longitudinal resistance
traces versus temperature. Each trace is taken at a separate magnetic
field as noted in the legend. The uppermost traces (taken at high
field) display insulating behavior (resistance increases as temperature
decreases) while the lower traces display quantum Hall like behavior.
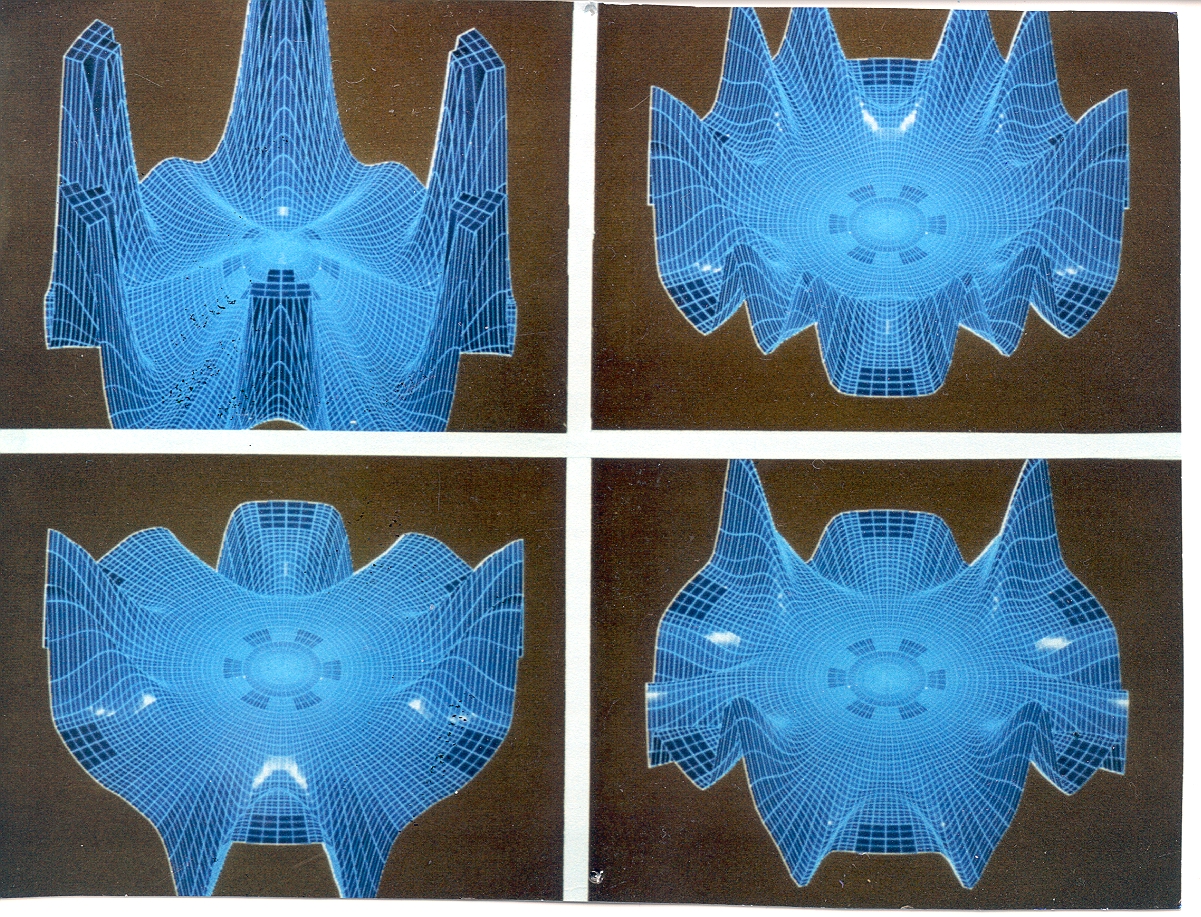
The potential energy surface and calculated surface functions which
are
used as a basis in our hyperspherical approach to quantum reactive
scattering.
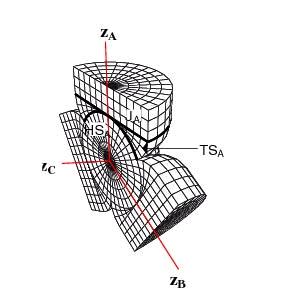
A tangent sphere method that eliminates the need for complicated
matching procedures. To accomplish this,
we use tangent-sphere coordinates to smoothly propagate from
hyperspherical coordinates to Jacobi coordinates. The
relationships between these coordinates are shown this figure.

The twin 10 meter telescopes of the Keck Observatory, Mauna Kea, Hawaii,
prepare to start another night of observing. Astronomers at OU
have
been granted observing time on these giant telescopes to study faint
objects at the edge
of the solar system, as well as the elemental abundances in old
stars in our galaxy.
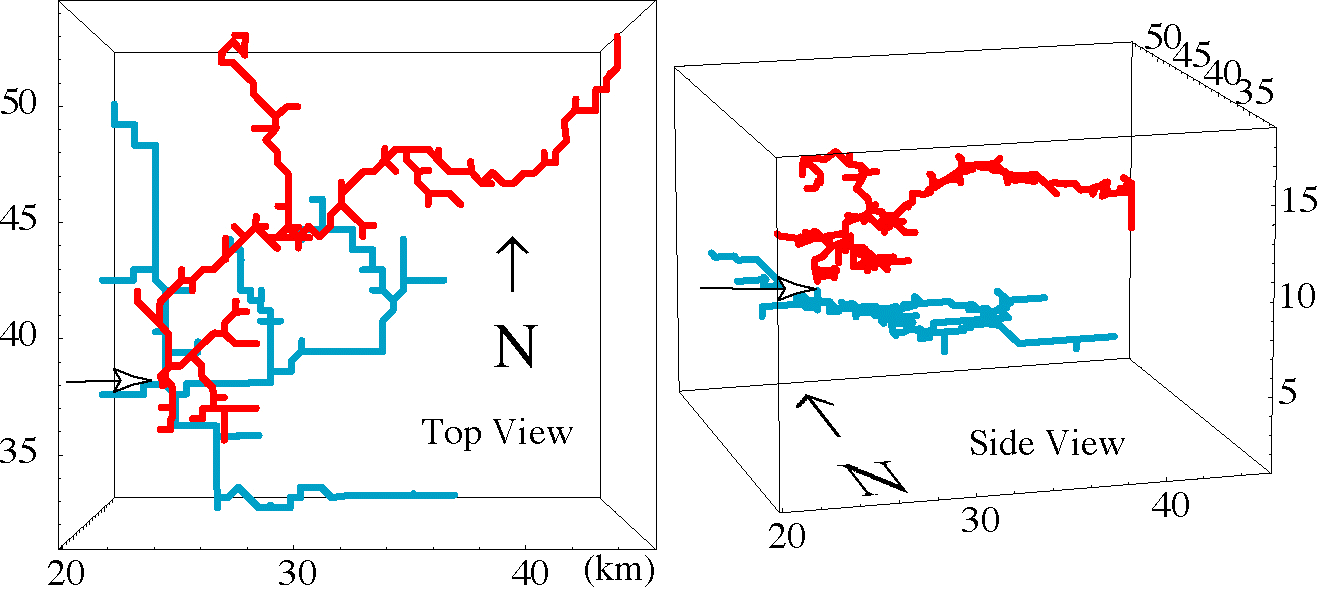
The first image is a simulated intracloud flash from a supercell simulation.
The positive leaders (blue) branches carry positive charge and propagate
into regions with primarily negative charge, and vice-versa for the
negative leaders (red). The open arrow indicates the initiation point of
the flash.
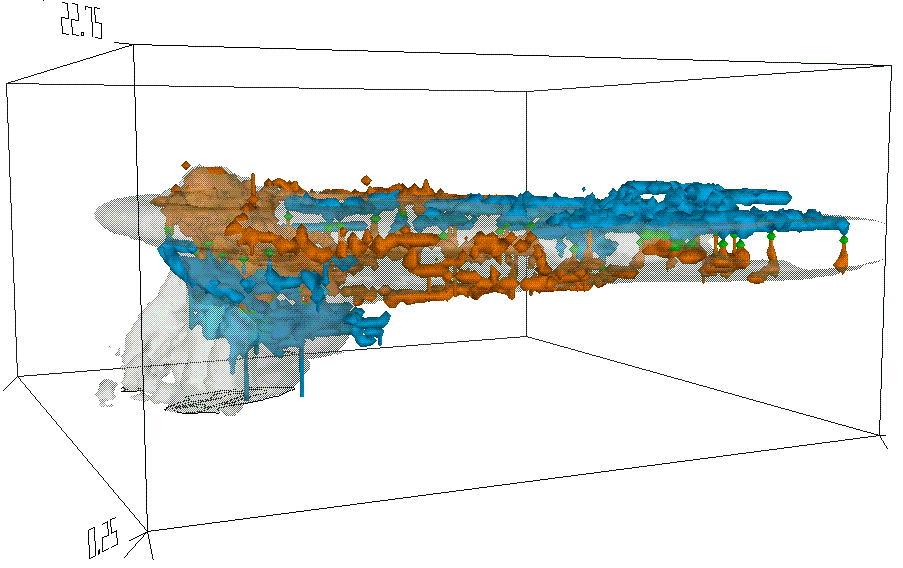
The second image is shows lightning during a 2.5 min period in a simulation
of a classic supercell storm (over 100 flashes). The volumes of lightning
activity are indicated for positive leaders (blue) and negative leaders
(red). The positive leaders which connect to ground indicate the occurence
of positive cloud-to-ground flashes. The line contours indicate surface
precipitation.
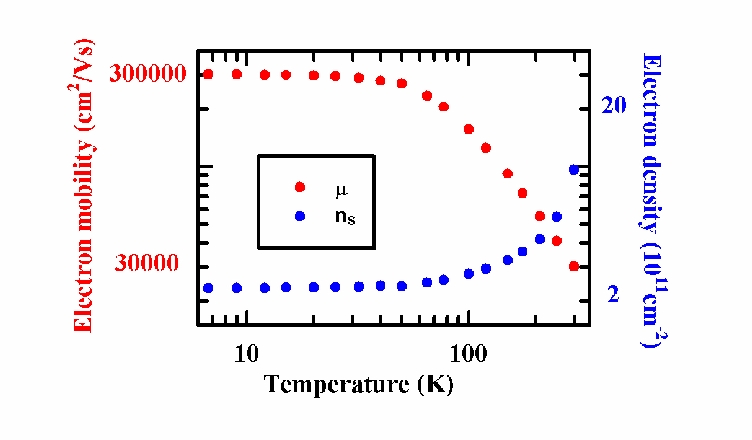
A plot of electron mobility and density as a function of temperature
in an OU grown InSb quantum well. One goal of modern semiconductor
research is to grow perfect layered structures with no defects, in order
achieve high mobility for the electrons tranvelling through the structure.
Samples grown at OU hold the world record for electron mobility at
room temperature of any quantum well structure.
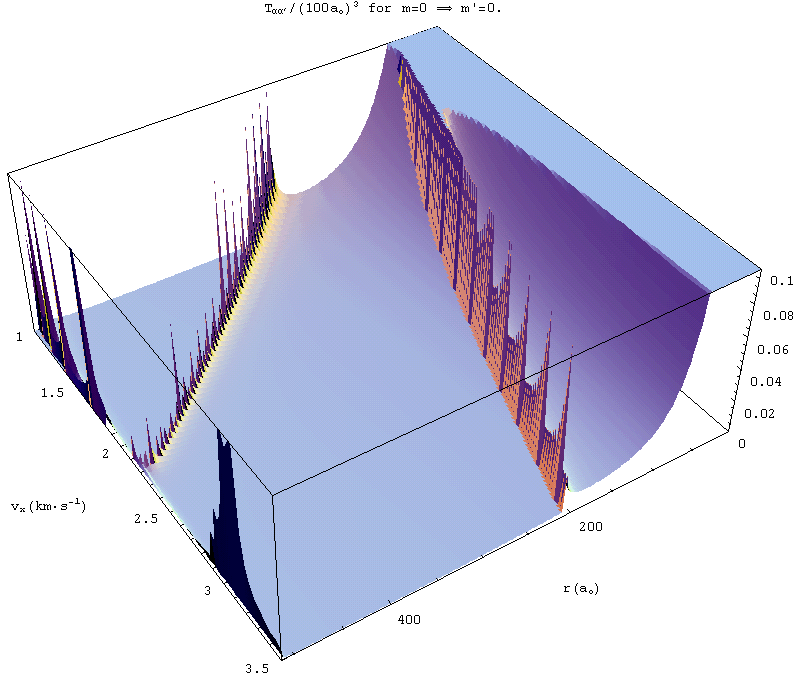
Classical probability of the near-resonant-energy-transfer process
Ca(n=18,
l=2, m=0) + He -> Ca(n=18, l=1, m=0) as a function of relative velocity
and
electron-Ca distance. Efforts are underway in our laboratory
to investigate
the analogous energy-transfer process between highly excited Hg atoms
and Xe
atoms.
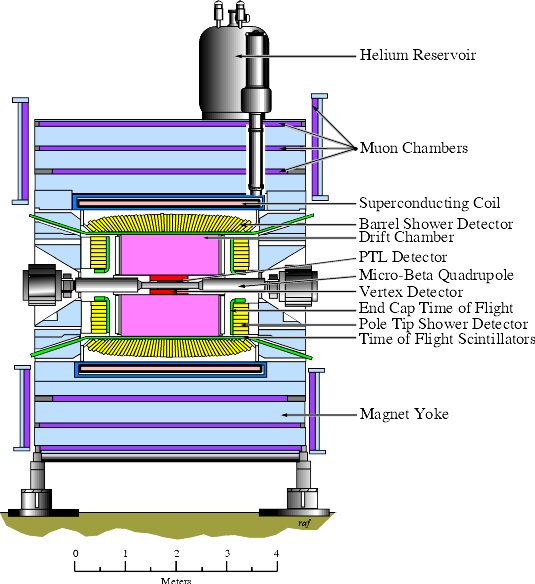
An artist's rendering of the central particle detector at CLEO.

A computer reconstruction of a top quark decay in the
D-Zero detector at the Fermilab Tevatron. Collisions
of protons and antiprotons produce top-antitop pairs
which decay into other particles seen in the D-zero
detector. The computer reconstructs the four-vectors
of the decay products and displays them in this drawing.
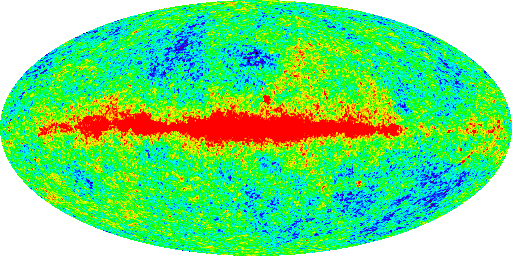
A simulation of the imprint of the primordial seeds in the cosmic microwave
background, as seen by the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP)
satellite. (credit: the MAP team, http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov)
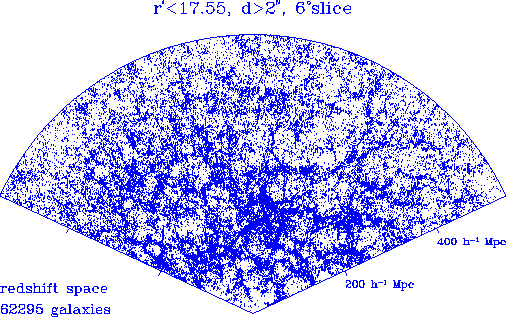
A simulation of a slice of the universe as seen by the Sloan Digital
Sky Survey (SDSS). (credit: the SDSS team, http://www.sdss.org)
Other Figures:
Nielsen Hall

REOS Image

Random Image 1
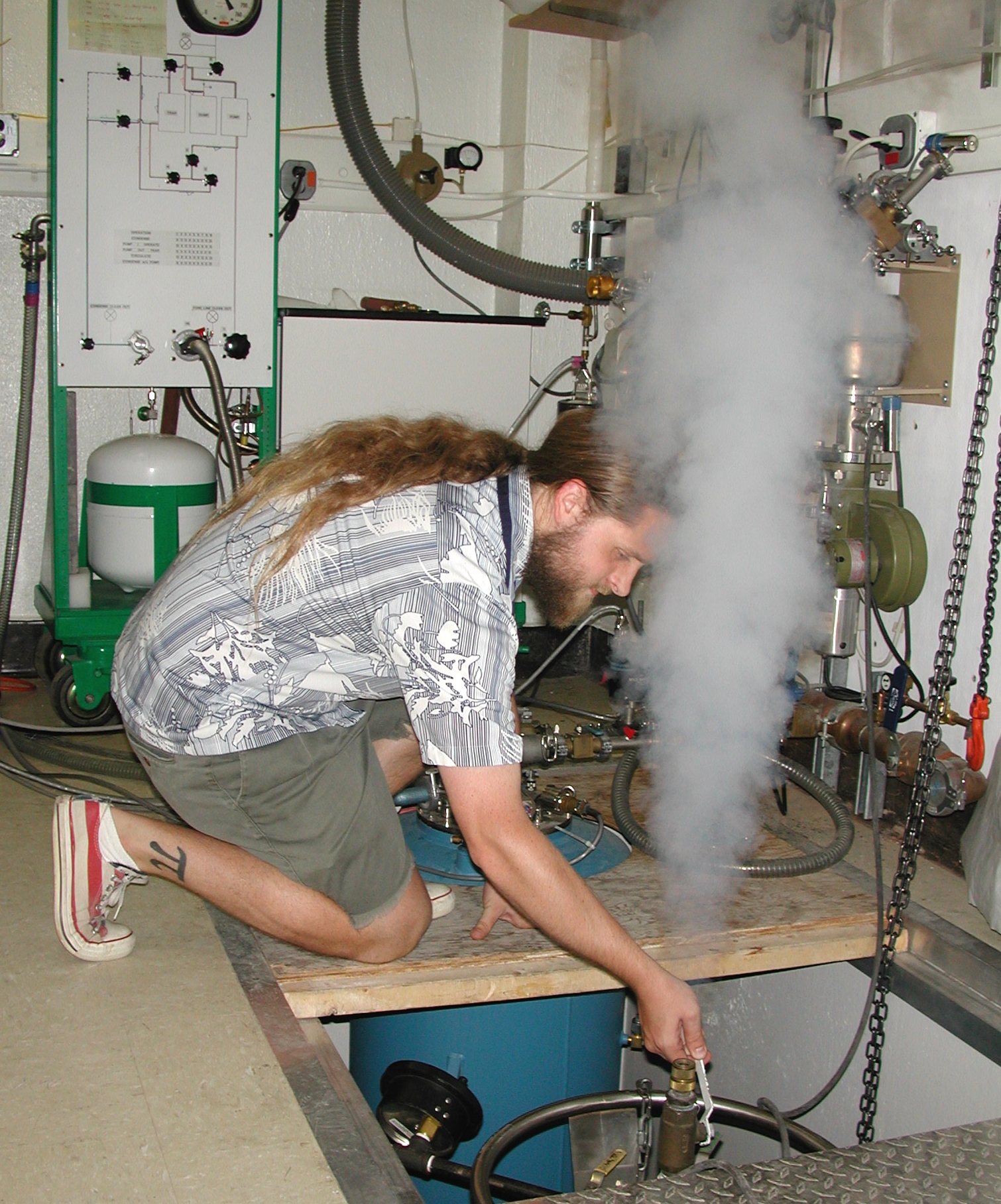

Graduate student Jim Hicks prepares to transfer liquid helium at 4.2K
into the experimental apparatus (blue vessel in rear). Low temperatures
are necessary to insure that we are examining the ground states of our
two dimensional electronic systems. The bath of liquid helium also
keeps our superconducting magnet system below the superconducting transition
temperature.
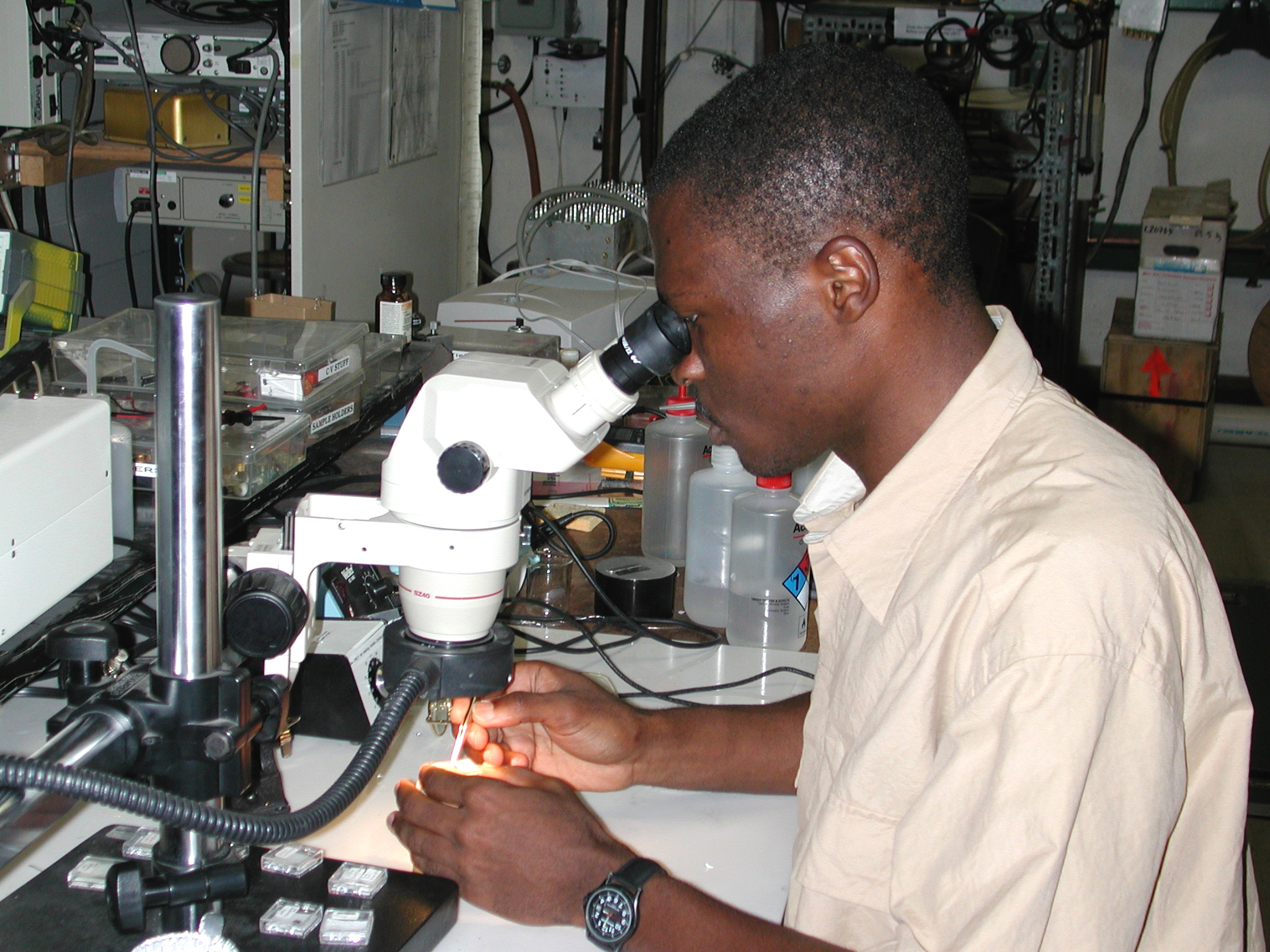


Graduate student Jean-Claude Chokomakoua uses an optical microscope
to examine a semiconductor sample. These samples from Prof. Santos'
MBE system are prepared for experiments in our semiconductor processing
facility located in the building. This advanced semiconductor processing
facility includes optical lithography equipment, evaporators and sputtering
systems.


CSPIN Logo:
